Breast cancer screening is a vital aspect of women’s health, designed to detect early signs of breast cancer before symptoms appear. Early detection through regular screening significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and survival. As Breast Cancer Screening(فحص سرطان الثدي) continues to be one of the most prevalent cancers among women worldwide, understanding the importance of screening and knowing the various options available are essential for proactive health management.
Why Breast Cancer Screening Matters?
Breast cancer screening plays a fundamental role in identifying cancerous changes or abnormalities in the breast tissue at an early stage. Early-stage breast cancer often has fewer symptoms and is more treatable, leading to higher survival rates. The most common screening methods are mammography, ultrasound, and MRI, each offering unique benefits depending on a woman’s age, risk factors, and overall health.
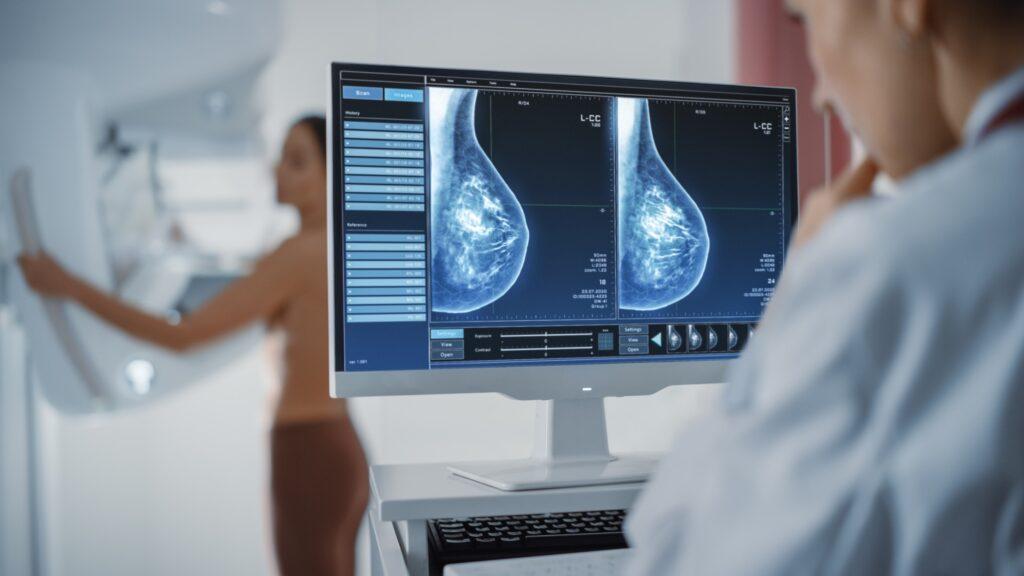
Benefits of Early Breast Cancer Detection:
- Increased Survival Rates: Detecting breast cancer early can significantly reduce mortality rates, offering better chances for effective treatment.
- Less Aggressive Treatments: Early detection often leads to less invasive treatments, such as breast-conserving surgery rather than a mastectomy.
- Improved Quality of Life: Early treatment allows patients to recover more quickly and maintain a better quality of life during and after treatment.
- Prevention of Spread: Screening identifies cancer before it spreads, making it easier to treat localized cancer and preventing it from reaching other organs.
Who Should Get Screened?
The general recommendation for breast cancer screening can vary based on age, risk factors, and family history. However, guidelines from health organizations offer a general overview:
- Women Aged 40-44: Women at average risk should have the option to start annual mammograms. Starting early provides an opportunity for early detection, even if no symptoms are present.
- Women Aged 45-54: It is generally recommended for women to begin annual mammograms, as this age group has an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
- Women Aged 55 and Older: Women in this age group can switch to biennial mammograms or continue annual screenings depending on their preferences and overall health.
- Women with High Risk: Women with a family history of breast cancer or other high-risk factors may be advised to begin screenings earlier or undergo more advanced screening tests such as MRI.
Screening Methods for Breast Cancer:
There are several methods used to screen for breast cancer, each with its own advantages. Here’s a look at the most common techniques:
- Mammography: A low-dose X-ray that remains the gold standard for breast cancer screening. Mammograms can detect tumors even before they can be felt, providing an early diagnosis.
- Ultrasound: Often used as a supplementary screening tool, ultrasound helps to distinguish between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts in the breast.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI may be recommended for women with a high risk of breast cancer or dense breast tissue. It uses magnetic fields to create detailed images of the breast, offering a clearer view of abnormalities.
- Clinical Breast Exam: A healthcare professional manually examines the breasts for signs of abnormalities. While not as effective as imaging tests, clinical breast exams can detect changes that may not be visible in other screenings.
Key Risk Factors for Breast Cancer:
While breast cancer can occur in women without any apparent risk factors, several factors can increase a woman’s likelihood of developing the disease:
- Age: The risk increases with age, especially after the age of 50.
- Family History: Having a first-degree relative (mother, sister, or daughter) diagnosed with breast cancer increases risk.
- Genetic Mutations: Mutations in genes such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 significantly increase the risk of developing breast cancer.
- Personal History of Breast Cancer: Women who have had breast cancer in one breast are at higher risk of developing cancer in the other breast.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can slightly increase the risk of breast cancer.
- Dense Breast Tissue: Women with dense breast tissue may have a higher risk and may need additional screening.

How Often Should You Be Screened?
The frequency of breast cancer screening depends on several factors, including age, risk level, and the type of screening being performed. Here’s a guideline:
- Annual or Biennial Mammograms: Most women should begin yearly or every two years mammograms at age 40. Women with a higher risk may start earlier.
- Clinical Exams: It is recommended that women have a clinical breast exam every 1 to 3 years starting at age 20 and annually after age 40.
- Self-Exams: Although not a substitute for professional screening, self-exams can help women detect any unusual changes in their breasts. Women should become familiar with the normal look and feel of their breasts.
Common Misconceptions About Breast Cancer Screening:
There are several myths surrounding Breast Cancer Screening(فحص سرطان الثدي) that can prevent women from seeking early detection. Let’s address a few:
- Screening is Only for Women with Symptoms: Screening is not just for women with lumps or symptoms. It’s intended to catch breast cancer early when no symptoms are present.
- Mammograms Are Painful and Dangerous: While mammograms can be uncomfortable, they are not dangerous and are one of the most effective methods for early detection. The risks of radiation are minimal compared to the benefits of detecting cancer early.
- Screening Always Detects Cancer: While mammograms are highly effective, they are not 100% accurate. False positives and false negatives can occur, so additional tests might be needed if an abnormality is detected.
- Only Older Women Need to Screen: Breast cancer can occur at any age, though it’s more common in women over 40. Women with high-risk factors should begin screening earlier.
The Psychological Impact of Breast Cancer Screening:
While breast cancer screening can save lives, it’s important to recognize the emotional impact it can have on women. Anxiety about test results, the possibility of a cancer diagnosis, and the uncertainty of next steps are common. To manage this stress:
- Open Communication: Women should talk to their healthcare providers about their concerns, questions, and any anxieties they may have.
- Support Networks: Having a support system of family, friends, or counselors can help manage emotional stress during the screening process.
- Follow-up Care: If a screening result is abnormal, it’s important to follow up with additional testing and guidance from healthcare providers to understand the situation clearly.
Conclusion:
Breast cancer screening is a critical element in safeguarding women’s health. Regular screenings allow for the early detection of breast cancer, improving the odds of successful treatment and survival. Understanding when to start screening, the different methods available, and the risks and benefits of each can empower women to take proactive steps in their healthcare. By continuing to raise awareness, debunk myths, and encourage regular screenings, we can ensure that women receive the best possible care for their long-term health and well-being.
